Introduction
Medicare Remote Patient Monitoring is gaining momentum, and it’s crucial for doctors and healthcare practices to determine the most suitable devices for their patients. In this post, we primarily focus on medically relevant B2B devices as opposed to consumer devices, and we explore the differences among Bluetooth, cellular, and hub devices to help you make informed choices.
Cellular-Enabled Devices

Advantages
Effortless Connectivity: Cellular-enabled RPM devices stand out for their user-friendly setup. With no reliance on home Wi-Fi or Bluetooth pairing, these devices offer a hassle-free connection process.
Reliable Data Transmission: The automatic transmission of patient data over cellular networks ensures seamless and timely information for healthcare providers.
Disadvantages
Higher Initial Cost: One notable drawback is the higher upfront cost associated with cellular-enabled devices. While they offer convenience, this financial aspect may pose a challenge for certain healthcare facilities or patients.
Bluetooth Devices

Advantages
Cost-Effective: Bluetooth-enabled RPM devices are generally more budget-friendly, making them an accessible option for a broader range of patients and healthcare providers.
User-Friendly: These devices are designed to be user-friendly, although patients need to ensure that their smartphone’s Bluetooth is active and the dedicated app is running for optimal functionality.
Disadvantages
Data Transmission Challenges: Bluetooth-dependent devices may face interruptions if Bluetooth is turned off or if the app is placed in idle mode, presenting a potential concern for users.
Limited Smartphone Dependency: The reliance on compatible smartphones may exclude older individuals who are not familiar with or lack access to these devices.
Hub Devices
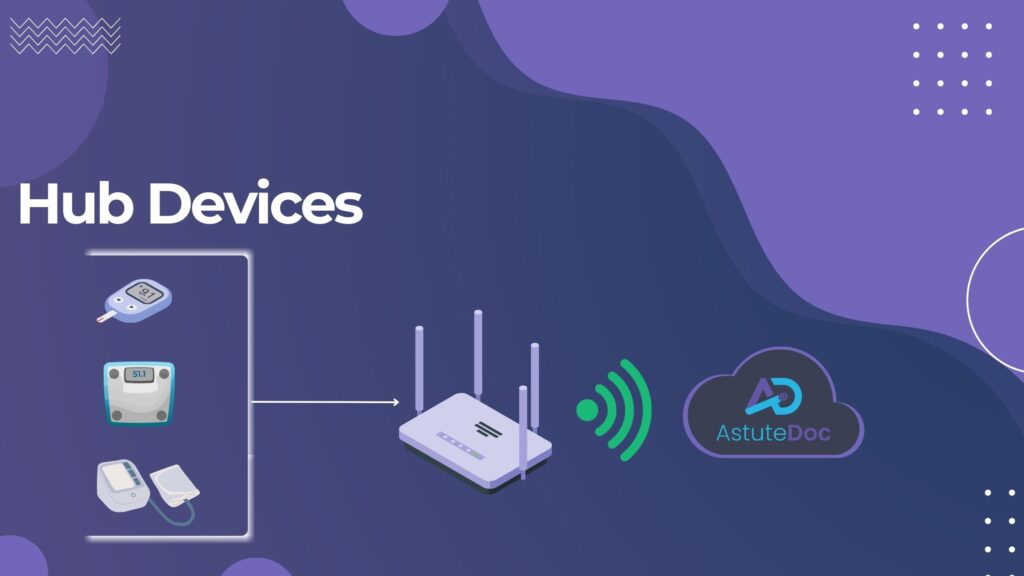
Advantages
Versatility: Hub devices shine when it comes to measuring multiple health parameters simultaneously, offering a cost-effective solution in scenarios requiring comprehensive monitoring.
Stability: These devices provide stable data transmission, minimising the risk of interruptions during the monitoring process.
Disadvantages
Higher Initial Cost: Hub devices tend to be the costliest option due to their advanced functionality, making them a substantial investment for healthcare facilities.
Complex Setup: Setting up hub devices can be more complex compared to other types, requiring configuration for both Bluetooth and network connectivity.
Conclusion
When it comes to Remote Patient Monitoring, choosing the right type of device is crucial for successful healthcare management. Cellular-enabled devices offer effortless connectivity but at a higher cost. Bluetooth devices are cost-effective but require smartphone compatibility and can have data transmission issues. Hub devices, while versatile, come with a higher initial investment.
It’s worth noting that AstuteDoc primarily works with cellular-enabled devices because they offer a reliable and user-friendly solution. This choice is especially important considering that many Medicare patients may face challenges in handling the complexities of Bluetooth devices. By prioritising simplicity and efficiency, healthcare providers can ensure that RPM programs are accessible and beneficial to a wide range of patients, ultimately improving healthcare outcomes for all.